| ||||||||||||||
| West Godavari district | |
|---|---|
| — District — | |
| Kolleru Lake at dusk | |
| Nickname(s): Granary of India | |
| Coordinates: Coordinates: | |
| Country | |
| State | Andhra Pradesh |
| Region | Andhra |
| Capital | Eluru |
| Government | |
| • Collector & District Magistrate | Dr. G. Vani Mohan, IAS |
| Area | |
| • Total | 7,742 km2 (2,989 sq mi) |
| Population (2011) | |
| • Total | 3,934,782 |
| • Density | 508/km2 (1,320/sq mi) |
| Languages | |
| • Official | Telugu |
| Time zone | IST (UTC+5:30) |
| PIN | 534 001 |
| Telephone code | 91-(08812) |
| Vehicle registration | AP-37 |
| Sub divisions | 4 |
| Municipalities | 8 |
| Nagara Panchayats | 1 |
| Mandals | 46 |
| Climate | Aw (Köppen) |
| Precipitation | 1,115 millimetres (43.9 in) |
| Avg. annual temperature | 26.0 °C (78.8 °F) |
| Avg. summer temperature | 45.9 °C (114.6 °F) |
| Avg. winter temperature | 23.5 °C (74.3 °F) |
| Website | westgodavari.org |
West Godavari District (Telugu: పశ్చిమ గోదావరి జిల్లా) is one of the 23 districts of Andhra Pradesh, India; the district headquarters is the city of Eluru. The district had a population of 3,934,782, 19.74% of which is urban population as of 2011 [1]. "Yaantiki" is the official word of West Godavari.
The district is in the delta region of the Krishna and Godavari rivers. Khammam District lies to the north, East Godavari District to the east, the Bay of Bengal to the south, and Krishna District to the west.
History[]
Rajamundhry (also called Rajamahendravaram) was a part of the Buddhist kingdom of Vengi. The Eastern Chalukyas ruled coastal Andhra from 700 to 1200, with Vengi, near the village of Pedavegi, as their capital. Historical evidences are found at the villages of Pedavegi and Guntupalli (Jilakarragudem). Eluru then became a part of the Kalinga Empire until 1471. Later it fell into the hands of the Gajapathis. In 1515 Sri Krishna Deva Raya captured it. After the fall of the Vijayanagara Kingdom, it was taken by the Sultan of Golkonda, Kutub Shah. In 1925, West Godavari District was formed with Eluru as its headquarters and all the district offices and regional offices were set up in Eluru town.
It was formed in April 14, 1921 - by dividing then Krishna and Godavari districts. The Godavari district was renamed as East Godavari District and the new district is named as West Godavari district.
Geography[]
West Godavari district occupies an area of approximately 7,700 square kilometres (3,000 sq mi),[1] comparatively equivalent to United States territory of Puerto Rico.
Climate[]
The region mostly has a tropical climate like the rest of the Coastal Andhra region. The summers (March–June) are very hot and humid while the winters are pleasant. The rainy season (July–December) is the best time to visit the district with the fields brilliantly green with paddy crops, rivers flowing with water and the relatively cool climate. The region has long been home to Indian nobles due to its climate and fertile soil, and several zamindar large mansions are scattered around the Godavari area.
Economy[]
The districts is extremely fertile, getting water abundantly throughout the Cotton barage built on the Godavari River at Dhavaleswaram. The barage chanels water through two canals. Topographically the district is divided into the Delta and the uplands.
In the Delta, aguaculture, coconut, lemon and rice are cultivated. The district is popularly known as the Granary of India since about 50% of the state's rice production comes from the district. In the uplands, oil palm, sugarcane, corn, mango, banana and other fruits as well as tobacco and cotton are produced. In the coastal belt of the district, prawns and fish is exported to Japan and the United States.
Development of manufacturing industries has been neglected despite availability of raw materials. However, ONGC started exploration activities in 1980 on the Krishna Godavari basin. Reliance & Cairn are making efforts to extract oil and gas.
Eluru is the biggest city in West Godavari District, with a thriving woolen pile carpet industry. Tadepalligudem is the geographic center of the district and its biggest market centre. Bhimavaram is a hub for Prawns export and is the home of Vendra paper mills. It is the richest town in the State of Andhra Pradesh. Tadepalligudem has a food fats and fertilisers industry. Tanuku has Andhra Sugars. Narasapur is one Major Town in West godavari DIST and It is famous for crochet lace products. Palakol is a famous for coconut exports (estimated at 200 crore per year).
Culture[]
The vast majority of the district is rural in nature thus the culture of the district is mostly conservative and traditional. The joint family system and arrainged marriages are the norm. Towns like Bhimavaram,Tadepalligudem and Eluru are a little bit more modern. The standard form of the Telugu dialect is spoken in this district just as its neighboring Krishna district.. English is commonly spoken by the younger generation as most higher education is conducted in English medium.
Household indicators[]
In 2007–2008 the International Institute for Population Sciences interviewed 999 households in 48 villages across the district.[2] They found that 93.2% had access to electricity, 98.1% to drinking water, 56.7% to indoor toilet facilities, and 33.2% lived in a pucca (permanent) home.[2] 28.4% of girls wed before the legal age of 18[3] and 86.4% of interviewees carried a BPL card.[2]
Image Gallery[]
Divisions[]
Constituencies[]
Earlier there had been two Parliamentary Constituencies and 16 Assembly Constituencies. The Constituencies Delimitation Committee has reduced that to 15 and now there are two parliamentary and 15 Assembly constituencies in West Godavari district.
The parliamentary constituencies are Eluru and Narsapur.
The Assembly constituencies[4] are:
- Achanta
- Bhimavaram
- Chintalapudi
- Denduluru
- Eluru
- Gopalapuram
- Kovvur
- Nidadavole
- Narsapur
- Palakollu
- Polavaram
- Tadepalligudem
- Tanuku
- Undi
- Unguturu
Municipal Corporation[]
- Eluru Population:214,414.
Municipalities[]
- Bhimavaram Population:142,064
- Kovvur Population:39,372
- Narasapuram Population:58,604
- Nidadavolu Population:60,835
- Palakol Population:76,308,
- Tadepalligudem Population:153,577
- Tanuku Population:72,970
Nagar Panchayat[]
- Jangareddygudem Population:97,961
Mandals[]
- Attili
- Akiveedu
- Achanta
- Buttayegudem
- Bheemavaram
- Bhimadole
- Chagallu
- Chintalapudi
- Devarapalle
- Denduluru
- Dwarakatirumala
- Eluru
- Gopalapuram
- Ganapavaram
- Iragavaram
- Jeelugumilli
- Jangareddigudem
- Kamavarapukota
- Kovvur
- Kalla
- Koyyalagudem
- Lingapalem
- Mogalthur
- Narasapuram
- Nallajarela
- Nidadavole
- Nidamarru
- Polavaram
- Pedavegi
- Pedapadu
- Pentapadu
- Peravali
- Poduru
- Palakoderu
- Penumantra
- Penugonda
- Palakol
- Thallapudi
- T.Narasapuram
- Tadepalligudem
- Tanuku
- Undrajavaram
- Unguturu
- Undi
- Veeravasaram
- Yelamanchili
Tourist Places[]
- Bhimavaram
- Dwaraka Tirumala Temple - Also called Chinna Tirupathi. It is temple of Lord Venkateswara Swamy
- Eluru is the District Head Quarter of West Godavari District.
- Ksheeraramam - One of the Pancharama kshetra in Palakol
- Kolleru Lake 15 km from Eluru - Kolleru Lake is the largest freshwater lake. Between Krishna and Godavari delta Kolleru is located. Spanning into two districts - Krishna and West Godavari.Siberian and Australian birds visit this lake during summer.
- Palakol - Main tourist attraction of Palakol is the Ksheera Rama Lingeswara Swami Temple with its 36.6 Mts high Tower (Pedha Gopuram).It is one of the five Pancharama_Kshetras.
- Papi Hills near Polavaram
- Polavaram Project
- Pattiseema, on the bank of the River Godavari - famous for Sri Veerabhadra Swamy Temple. It is a movie shooting spot
- Somaramam - One of the Pancharama kshetra in Bhimavaram
- Ambica Devi Temple
- Chinchinada bridge - connecting West Godavari and Konaseema of East Godavari District.
- Guntupally Caves - Buddist site - near Kamavarapukota
- Janardhana Swamy Temple
- Jalapahareswara Swamy Temple
- Kshira Ramalingeswara Swamy Temple
- Longest Rail cum Road Bridge (Kovvur and Rajahmundry) connecting East and West Godavari Districts
- Mavullamma Thalli Devasthanam famous temple in Bhimavaram
- Mavullamma Ammavari Temple
- NAM Datta Natha Kshetra
- Natta Rameswaram - famous Sri Rameswaraswamy Devasthanam near Attili
- Perupalem Beach of Mogalthur Mandal
- Sri Kanaka Durga Temple
- Sanivarapupeta Galigopuram
- Somaramam
- Subramanyeswara Swamy Devasthanam in Attili
- Sri Maddi Anjaneya Swamy Devasthanam - 5 km from Jangareddygudem and 20 km from Dwaraka Tirumala
- Venkateswara Swamy Temple
Demographics[]
According to the 2011 census West Godavari district has a population of 3,934,782,[5] roughly equal to the nation of Liberia[6] or the US state of Oregon.[7] This gives it a ranking of 61st in India (out of a total of 640).[5] The district has a population density of 508 inhabitants per square kilometre (1,320 /sq mi) .[5] Its population growth rate over the decade 2001-2011 was 3.45%.[5] West Godavari has a sex ratio of 1004 females for every 1000 males,[5] and a literacy rate of 74.32%.[5]
| Religion in West godavari | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Religion | Percent | |||
| Hinduism | 94% | |||
| Christian | 4% | |||
| Muslim | 2% | |||
| Distribution of religions | ||||
References[]
- ^ Srivastava, Dayawanti et al. (ed.) (2010). "States and Union Territories: Andhra Pradesh: Government". India 2010: A Reference Annual (54th ed.). New Delhi, India: Additional Director General, Publications Division, Ministry of Information and Broadcasting (India), Government of India. pp. 1111–1112. ISBN 978-81-230-1617-7.
- ^ a b c "District Level Household and Facility Survey (DLHS-3), 2007-08: India. Andhra Prades" (PDF). International Institute for Population Sciences and Ministry of Health and Family Welfare. 2010. http://www.rchiips.org/pdf/rch3/report/AP.pdf. Retrieved 2011-10-03.
- ^ "How Do I? : Obtain Marriage Certificate". National Portal Content Management Team, National Informatics Centre. 2005. http://india.gov.in/howdo/howdoi.php?service=3. Retrieved 2011-10-03. "To be eligible for marriage, the minimum age limit is 21 for males and 18 for females."
- ^ District-wise Assembly-Constituencies in Andhra Pradesh
- ^ a b c d e f "District Census 2011". Census2011.co.in. 2011. http://www.census2011.co.in/district.php. Retrieved 2011-09-30.
- ^ US Directorate of Intelligence. "Country Comparison:Population". https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/rankorder/2119rank.html. Retrieved 2011-10-01. "Liberia 3,786,764 July 2011 est."
- ^ "2010 Resident Population Data". U. S. Census Bureau. http://2010.census.gov/2010census/data/apportionment-pop-text.php. Retrieved 2011-09-30. "Oregon 3,831,074"
External links[]
- Official site

Wikivoyage has a travel guide for West Godavari (district). - District profile at AP Online.
- Godavari district temples map
- Times of India article
- papikondalu.net.in

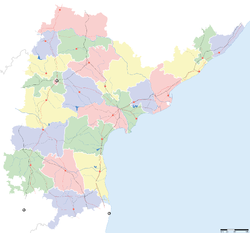
Khammam district 
Krishna district East Godavari district 

West Godavari district
Bay of Bengal Capital: Hyderabad (Temporary)Topics - Cinema
- Cuisine
- Culture
- Economy
- Education
- Elections
- Geography
- Government
- History
- Language
- Politics
- People
- Tourism
Districts Major cities
Template:Godavari basin
| This page uses content from the English language Wikipedia. The original content was at West Godavari district. The list of authors can be seen in the page history. As with this Familypedia wiki, the content of Wikipedia is available under the Creative Commons License. |