| Rivière-du-Loup | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| — City — | |||
| Rivière-du-Loup at sunset | |||
|
|||
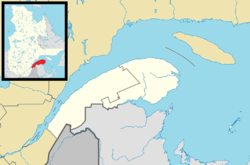
| Location within Rivière-du-Loup RCM | |||
| Country | |||
| Province | |||
| Region | Bas-Saint-Laurent | ||
| RCM | Rivière-du-Loup | ||
| Settled | 1850 as Fraserville | ||
| Constituted | December 30, 1998 | ||
| Government[1] | |||
| • Mayor | Mario Bastille | ||
| • Federal riding | Montmagny—L'Islet—Kamouraska—Rivière-du-Loup | ||
| • Prov. riding | Rivière-du-Loup–Témiscouata | ||
| Area[1][2] | |||
| • City | 138.40 km2 (53.44 sq mi) | ||
| • Land | 84.23 km2 (32.52 sq mi) | ||
| • Urban[3] | 17.77 km2 (6.86 sq mi) | ||
| • Metro[4] | 472.91 km2 (182.59 sq mi) | ||
| Population (2016)[2] | |||
| • City | 19,507 | ||
| • Density | 231.9/km2 (601/sq mi) | ||
| • Urban[3] | 17,973 | ||
| • Urban density | 983.9/km2 (2,548/sq mi) | ||
| • Metro[4] | 28,902 | ||
| • Metro density | 53.1/km2 (138/sq mi) | ||
| • Pop 2011-2016 | |||
| • Dwellings | 9,772 | ||
| Time zone | EST (UTC−5) | ||
| • Summer (DST) | EDT (UTC−4) | ||
| Postal code(s) | G5R | ||
| Area code(s) | 418 and 581 | ||
Highways  [[Template:Infobox road/QC/link TCH|Template:Infobox road/QC/abbrev TCH]] [[Template:Infobox road/QC/link TCH|Template:Infobox road/QC/abbrev TCH]]  [[Template:Infobox road/QC/link TCH|Template:Infobox road/QC/abbrev TCH]] [[Template:Infobox road/QC/link TCH|Template:Infobox road/QC/abbrev TCH]] |
 Route 132 Route 132  Route 191 Route 191 Route 291 Route 291 |
||
| Website | villerdl.ca | ||
Rivière-du-Loup (French pronunciation: [ʁivjɛʁ dy lu]; 2016 population 19,507) is a small city on the south shore of the Saint Lawrence River in Quebec. The city is the seat for the Rivière-du-Loup Regional County Municipality and the judicial district of Kamouraska.[5] Its one of the largest cities in Bas-Saint-Laurent.
History[]
The city was named after the nearby river, whose name means Wolf's River in French. This name may have come from a native tribe known as "Les Loups" ("The Wolves") or from the many seals, known in French as loup-marin (sea wolves), once found at the river's mouth.
Rivière-du-Loup was established in 1673 as the seigneurie of Sieur Charles-Aubert de la Chesnaye. The community was incorporated as the village of Fraserville, in honour of early Scottish settler Alexander Fraser, in 1850, and became a city in 1910. The city reverted to its original name, Rivière-du-Loup, in 1919.
Between 1850 and 1919, the city saw large increases in its anglophone population. Most of them left the region by the 1950s. 1% of the population still speaks English as its first language.
In fall of 1950 Rivière-du-Loup was the site of a nuclear accident. A USAF B-50 was returning a nuclear bomb to the USA. The bomb was released due to engine troubles, and then was destroyed in a non-nuclear detonation before it hit the ground. The explosion scattered nearly 100 pounds (45 kg) of uranium (U-238).
Transportation[]

Rue LaFontaine is an important commercial street in Rivière-du-Loup.
Rivière-du-Loup is a traditional stopping point between Quebec City, the Maritimes and the Gaspé Peninsula. The Trans-Canada Highway turns south here, transferring from Autoroute 20 to Autoroute 85 and continuing southwards to Edmundston, New Brunswick.
There is a ferry that crosses the river (fleuve St Laurent) to Saint-Siméon on the north shore.
The city is also served by the Rivière-du-Loup Airport (IATA airport code YRI). The town can also be reached by Via Rail on the train named The Ocean, between Montreal and Halifax.
Media[]
Television[]
Rivière-du-Loup is an unusual television market, as each of its stations has two transmitters in the city. The city's hilly terrain causes residents of the lower, western portions of the city to experience frequent signal dropout. That makes it all but impossible for a television station to serve the entire area with a single transmitter. Accordingly, each station in the city has both a primary transmitter and a "nested" low-power rebroadcaster to serve viewers in the western part of the city who cannot receive the primary signal.
Until August 2021, the city was served by Canada's only triple-stick operation, in which all three of its licensed stations are owned by the same company, Télé Inter-Rives. This would be pared down to a twin-stick following the closedown of CKRT-DT in August 2021.
| OTA virtual channel (PSIP) | OTA actual channel | Vidéotron Cable | Call sign | Network | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9.1 | 9 (VHF) | 4 | CIMT-DT | TVA | Maintains low-power rebroadcaster on UHF channel 41 |
| 29.1 | 29 (UHF) | 5 | CFTF-DT | Noovo | Maintains low-power rebroadcaster on VHF channel 11 |
Defunct station:
| OTA virtual channel (PSIP) | OTA actual channel | Vidéotron Cable | Call sign | Network | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7.1 | 7 (VHF) | 10 | CKRT-DT | Ici Radio-Canada Télé | Maintained low-power rebroadcaster on VHF channel 13 |
Rivière-du-Loup is a mandatory market for digital television conversion; Télé Inter-Rives converted all of its transmitters to digital prior to the deadline of August 30, 2011.
Unlike most larger cities in Quebec, Rivière-du-Loup has no local Télé-Québec outlet, though Rimouski's CIVB-DT is available on the Vidéotron system in Rivière-du-Loup. Following the closedown of CKRT-DT, Radio-Canada would be seen on Vidéotron from CJBR-DT Rimouski.
Radio[]
- FM 89.5 - CJBR-FM-1, Ici Radio-Canada Première
- FM 90.7 - CBRX-FM-3, Ici Musique
- FM 103.7 - CIEL-FM, AC
- FM 107.1 - CIBM-FM, CHR
- FM 107.9 - CIBM-FM-1 (local CIBM rebroadcaster)
Notable people[]
Sir John A. Macdonald, Canada's first prime minister, had a summer home in Rivière-du-Loup.
People born there include:
- Danielle April, artist[6]
- Joseph Jean Benoit, 31st Canadian Surgeon General
- Nicolas Dickner, writer
- Dr. John McLoughlin, known as "the father of Oregon"
- Louis-Philippe Picard, member of the House of Commons of Canada
- Maurice Arthur Pope, soldier and diplomat
- Allan Sirois, professional hockey player
- Alexandre-Antonin Taché, first Archbishop of Saint Boniface
See also[]
- List of cities in Quebec
References[]
- ^ a b Geographic code 12072 in the official Répertoire des municipalités (French)
- ^ a b "(Code 2412072) Census Profile". 2011 census. Statistics Canada. 2012. http://www12.statcan.gc.ca/census-recensement/2011/dp-pd/prof/details/page.cfm?Lang=E&Geo1=CSD&Code1=2412072&Geo2=PR&Code2=24&Data=Count&SearchType=Begins&SearchPR=01&B1=All.
- ^ a b "(Code 0712) Census Profile". 2011 census. Statistics Canada. 2012. http://www12.statcan.gc.ca/census-recensement/2011/dp-pd/prof/details/page.cfm?Lang=E&Geo1=POPC&Code1=0712&Geo2=PR&Code2=01&Data=Count&SearchType=Begins&SearchPR=01&B1=All.
- ^ a b "(Code 405) Census Profile". 2011 census. Statistics Canada. 2012. http://www12.statcan.gc.ca/census-recensement/2011/dp-pd/prof/details/page.cfm?Lang=E&Geo1=CMA&Code1=405&Geo2=PR&Code2=01&Data=Count&SearchType=Begins&SearchPR=01&B1=All.. The census agglomeration consists of Rivière-du-Loup, Cacouna, Notre-Dame-du-Portage, Saint-Antonin, Saint-Modeste. In the 2006 census, the census agglomeration had not included Cacouna.
- ^ Territorial Division Act. Revised Statutes of Quebec D-11.
- ^ "APRIL, Danielle (1949)". http://dictionnaire.espaceartactuel.com/en/artistes/april-danielle-1949/.
<ref> tag with name "toponymie" defined in <references> is not used in prior text.External links[]
| ||||||||||||||
|