| Lower Austria Niederösterreich |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| — State of Austria — | |||
|
|||
| Country | |||
| Capital | Sankt Pölten | ||
| Government | |||
| • Governor | Erwin Pröll (ÖVP) | ||
| Area | |||
| • Total | 19,186 km2 (7,408 sq mi) | ||
| Population | |||
| • Total | 1,612,000 | ||
| • Density | 84/km2 (220/sq mi) | ||
| Time zone | CET (UTC+1) | ||
| • Summer (DST) | CEST (UTC+2) | ||
| ISO 3166 code | AT-3 | ||
| NUTS Region | AT1 | ||
| Votes in Bundesrat | 12 (of 62) | ||
| Website | www.noe.gv.at | ||
Lower Austria (German: Niederösterreich (help·info)) is the northeasternmost state of the nine states in Austria. The capital of Lower Austria since 1986 is Sankt Pölten, the most recently designated capital town in Austria. The capital of Lower Austria had formerly been Vienna, even though Vienna is not officially part of Lower Austria. With a land area of 19,186 km² and a population of 1.612 million people, it is the largest state in Austria, and in terms of population second only to the federal state of Vienna.
Geography
Situated east of Upper Austria, Lower Austria derives its name from its downriver location on the Danube River, which flows from west to east. The state borders on Slovakia, the Czechia (South Moravia), and the other Austrian states of Upper Austria, Styria and Burgenland. The state surrounds Vienna.
Lower Austria is the largest state in Austria with an area of 19,186.26 square kilometres. It is divided four regions, known as Viertel (quarters):
- Weinviertel or Tertiary Lowland (below the Manhartsberg),
- Waldviertel or Bohemian Plateau (above the Manhartsberg),
- Mostviertel (above the Vienna Woods)
- Industrieviertel (below the Vienna Woods).
These regions have different geographical structures. Whilst the Mostviertel is dominated by the foothills of the Limestone Alps with mountains up to 2,000 m above sea level (AA) high, most of the Waldviertel is a granite plateau. The hilly Weinviertel lies to the northeast, descends to the plains of Marchfeld in the east of the state, and is separated by the Danube from the Vienna Basin to the south, which in turn is separated from the Vienna Woods by a line of thermal springs (the Thermenlinie) running north to south.
Lower Austria has an international border, 414 km long, with the Czech Republic and Slovakia. The state has the second longest external border of all Austrian states.
Mountains
- Schneeberg (Klosterwappen; 2,076 m)
- Rax (Scheibwaldhöhe; 1,943 m; highest summit: Heukuppe; 2,007 m – Styria)
- Ötscher (1,893 m)
- Dürrenstein (1,878 m)
- Schneealpe (Ameisbühel; 1,828 m; highest summit: Windberg; 1,903 m – Styria)
- Hochkar (1,808 m)
- Gamsstein (1,774 m)
- Stumpfmauer (1,770 m)
- Göller (1,766 m)
- Hochwechsel (1,743 m)
- Gippel (1,669 m)
- Großer Sonnleitstein (1,639 m)
- Großer Zellerhut (1,639 m)
- Gemeindealpe (1,626 m)
- Drahtekogel (1,565 m)
- Sonnwendstein (1,523 m)
- Obersberg (1,467 m)
- Königsberg (1,452 m)
- Großer Sulzberg (1,400 m)
- Reisalpe (1,399 m)
- Gahns (1,380 m)
- Tirolerkogel (1,377 m)
- Türnitzer Höger (1,372 m)
- Unterberg (1,342 m)
- Traisenberg (1,230 m)
- Dürre Wand (1,222 m)
- Hohenstein (1,195 m)
- Eisenstein (1,185 m)
- Hohe Wand (1,132 m)
- Großer Peilstein (1,061 m)
- Weinsberg (1,041 m)
- Hocheck (1,036 m)
- Nebelstein (1,017 m)
- Eibl (1,007 m)
- Hohe Mandling (967 m)
- Jauerling (961 m)
- Anninger (675 m)
- Buschberg (491 m)
Other mountains in Lower Austria may be found at Category:Mountains of Lower Austria.
Alpine passes
- Semmering (985 m)
- Wechsel (980 m)
The state border with Styria runs over both passes.
Rivers

Kamp

March
Almost all of Lower Austria is drained by the Danube. The only river that flows into the North Sea via the Moldau and the Elbe is the Lainsitz in northern Waldviertel.
The most important rivers north of the Danube (on its left banks) are the Ysper, Kamp, Krems, Lainsitz, March and Thaya. South of the Danube (on its right banks) are the Enns, Ybbs, Erlauf, Melk, Pielach, Traisen, Schwechat, Fischa, Schwarza, Triesting, Pitten and the Leitha.
Lakes
- Ottenstein Reservoir (4.3 km²)
- Lunzer See (0.69 km²)
- Erlaufsee (0.56 km², of which about half lies in Lower Austria)
- Erlauf Reservoir
- Wienerwaldsee (0.32 km²)
Land use
| Type of land use | Area in km² | Percent of total area |
|---|---|---|
| Farmland | 7,000 | 42 |
| Woods | 6,711 | 40 |
| Grassland | 1,750 | 11 |
| Alpine pastures | 300 | 1.7 |
| Vineyards | 315 | 1.9 |
History
The history of Lower Austria is very similar to the History of Austria. Many castles are located in Lower Austria. Klosterneuburg Abbey, located here, is one of the oldest abbeys in Austria. Before World War II, Lower Austria had the largest number of Jews in Austria.
Administrative divisions
Lower Austria is divided into four regions: Waldviertel, Mostviertel, Industrieviertel, and Weinviertel. The Wachau valley, situated between Melk and Krems in the Mostviertel region, is famous for its landscape, culture, and wine.
Administratively, the state is divided into 21 districts (Bezirke), and four independent towns (Statutarstädte). In total, there are 573 municipalities within Lower Austria.
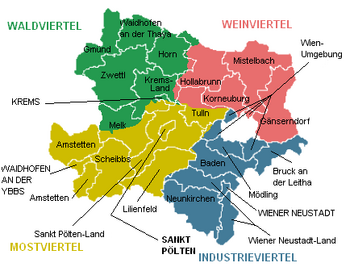
Map of Lower Austria showing districts and the four quarters (Waldviertel in green, Weinviertel in red, Mostviertel in yellow and Industrieviertel in blue)
Independent towns
- Krems
- Sankt Pölten
- Waidhofen an der Ybbs
- Wiener Neustadt
Districts
- Amstetten
- Baden
- Bruck an der Leitha
- Gänserndorf
- Gmünd
- Hollabrunn
- Horn
- Korneuburg
- Krems-Land
- Lilienfeld
- Melk
- Mistelbach
- Mödling
- Neunkirchen
- St. Pölten-Land
- Scheibbs
- Tulln
- Waidhofen an der Thaya
- Wiener Neustadt-Land
- Wien-Umgebung
- Zwettl
External links
| Wikisource has the text of the 1911 Encyclopædia Britannica article Austria, Lower. |
- Land Niederösterreich
- Lower Austrian Genealogy
- PhotoGlobe - georeferenced photos of Lower Austria
| |||||
| This page uses content from the English language Wikipedia. The original content was at Lower Austria. The list of authors can be seen in the page history. As with this Familypedia wiki, the content of Wikipedia is available under the Creative Commons License. |


