| ||||||||||||||
| Lee County, Alabama | |
Main façade of Lee Courthouse, 2009
| |
| Motto: "The Heart of Dixie" | |
|---|---|
 Location in the state of Alabama | |
 Alabama's location in the U.S. | |
| Founded | December 5, 1866 |
| Named for | General Robert E. Lee |
| Seat | Opelika |
| Largest city | Auburn |
| Area - Total - Land - Water |
616 sq mi (1,595 km²) 608 sq mi (1,575 km²) 8.3 sq mi (21 km²), 1.3 |
| Population - (2020) - Density |
174,241 |
| Congressional district | 3rd |
| Time zone | Central: UTC-6/-5 |
| Website | www.leeco.us |
| Footnotes: * County Number 43 on Alabama License Plates | |
Lee County is a county located in east central Alabama. As of the 2020 census the population was 174,241.[1] The county seat is Opelika,[2] and the largest city is Auburn. The county is named for General Robert E. Lee (1807–1870), who served as General in Chief of the Armies of the Confederate States in 1865.[3] Lee County comprises the Auburn-Opelika, AL Metropolitan Statistical Area, which is included in the Columbus-Auburn-Opelika, GA-AL Combined Statistical Area.
History[]
Lee County was established by the State Legislature on December 5, 1866, out of parts of Macon, Tallapoosa, Chambers, and Russell counties. In an election to determine the county seat, Opelika was chosen over Auburn and Salem. In 1923, Phenix City, located in the southeastern corner of Lee County, merged with the town of Girard, located in the northeastern corner of Russell County.
To prevent the new town of Phenix City from straddling the Lee-Russell line, Lee County ceded to Russell County the 10 square miles (25.9 km2) in the southeastern corner surrounding Phenix City in exchange for 20 square miles (51.8 km2) in the northwest corner of Russell County surrounding the unincorporated community of Marvyn. This territory is what forms the southern "panhandle" of Lee County.
On March 3, 2019, a series of tornadoes hit the county, killing 23 people and injuring others. The deaths and injuries occurred in the community of Beauregard, situated south-east of the Auburn-Opelika metropolitan area.
Geography[]
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of 616 square miles (1,600 km2), of which 608 square miles (1,570 km2) is land and 8.3 square miles (21 km2) (1.3%) is water.[4]
The county straddles the fall line between the Piedmont region to the north, and the Gulf coastal plain to the south. Thus, northern areas of the county are hillier compared to southern areas of the county.
Major highways[]
Adjacent counties[]
- Chambers County (north)
- Harris County, Georgia (northeast)
- Muscogee County, Georgia (east)
- Russell County (south)
- Macon County (southwest)
- Tallapoosa County (northwest)
Railroads[]
- CSX A&WP Subdivision
- Norfolk Southern Central of Georgia District
Demographics[]
| Historical populations | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1870 | 21,750 | ||
| 1880 | 27,262 | 25.3% | |
| 1890 | 28,694 | 5.3% | |
| 1900 | 31,826 | 10.9% | |
| 1910 | 32,867 | 3.3% | |
| 1920 | 32,821 | −0.1% | |
| 1930 | 36,063 | 9.9% | |
| 1940 | 36,455 | 1.1% | |
| 1950 | 45,073 | 23.6% | |
| 1960 | 49,754 | 10.4% | |
| 1970 | 61,268 | 23.1% | |
| 1980 | 76,283 | 24.5% | |
| 1990 | 87,146 | 14.2% | |
| 2000 | 115,092 | 32.1% | |
| 2010 | 140,247 | 21.9% | |
| U.S. Decennial Census[5] 1790–1960[6] 1900–1990[7] 1990–2000[8] 2010–2020[1] | |||
2000 Census[]
At the 2000 census there were 115,092 people, 45,702 households, and 27,284 families living in the county. The population density was 189 people per square mile (73/km2). There were 50,329 housing units at an average density of 83 per square mile (32/km2). The racial makeup of the county was 74.1% White, 22.7% Black or African American, 0.2% Native American, 1.6% Asian, <0.1% Pacific Islander, 0.5% from other races, and 0.9% from two or more races. 1.4% of the population were Hispanic or Latino of any race.[9] Of the 45,702 households 29.7% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 44.1% were married couples living together, 11.8% had a female householder with no husband present, and 40.3% were non-families. 27.8% of households were one person and 5.7% were one person aged 65 or older. The average household size was 2.42 and the average family size was 3.03.
The age distribution was 23.3% under the age of 18, 22.7% from 18 to 24, 28.1% from 25 to 44, 17.8% from 45 to 64, and 8.1% 65 or older. The median age was 28 years. For every 100 females, there were 96.90 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 95.20 males.
The median household income was $30,952 and the median family income was $46,781. Males had a median income of $33,598 versus $23,228 for females. The per capita income for the county was $17,158. About 11.1% of families and 21.8% of the population were below the poverty line, including 16.3% of those under age 18 and 12.0% of those age 65 or over.
2010 census[]
At the 2010 census there were 140,247 people, 55,682 households, and 33,692 families living in the county. The population density was 227.7 people per square mile (87.9/km2). There were 62,391 housing units at an average density of 101.3 per square mile (39.1/km2). The racial makeup of the county was 71.3% White, 22.7% Black or African American, 0.3% Native American, 2.6% Asian, 0.1% Pacific Islander, 1.3% from other races, and 1.6% from two or more races. 3.3% of the population were Hispanic or Latino of any race.[9] Of the 55,682 households 28.0% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 43.1% were married couples living together, 13.0% had a female householder with no husband present, and 39.5% were non-families. 27.9% of households were one person and 6.0% were one person aged 65 or older. The average household size was 2.44 and the average family size was 3.03.
The age distribution was 22.5% under the age of 18, 20.5% from 18 to 24, 26.1% from 25 to 44, 21.8% from 45 to 64, and 9.1% 65 or older. The median age was 28.3 years. For every 100 females, there were 97.2 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 98.0 males.
The median household income was $40,894 and the median family income was $59,112. Males had a median income of $42,335 versus $31,766 for females. The per capita income for the county was $22,794. About 11.0% of families and 19.2% of the population were below the poverty line, including 19.0% of those under age 18 and 9.0% of those age 65 or over.
2020 Census[]
| Race | Num. | Perc. |
|---|---|---|
| White (non-Hispanic) | 109,795 | 63.01% |
| Black or African American (non-Hispanic) | 39,252 | 22.53% |
| Native American | 365 | 0.21% |
| Asian | 8,544 | 4.9% |
| Pacific Islander | 108 | 0.06% |
| Other/Mixed | 7,042 | 4.04% |
| Hispanic or Latino | 9,135 | 5.24% |
As of the 2020 United States census, there were 174,241 people, 64,448 households, and 37,809 families residing in the county.
Government[]
Among the principal governmental functions vested in Alabama counties are law enforcement; tax assessment, levy and collection; administration of decedent's estates and probate matters; maintenance of real and personal property title records; construction and maintenance of public roads and bridges; and maintenance of the county courthouse, which provides office space for various county officials and departments. Lee County is one of only seven counties in Alabama that has been granted limited home rule. It is governed by a six-member county commission, composed of the Probate Judge and five commissioners. The Probate Judge is elected countywide for a six-year term and serves as chairman of the commission. The other commissioners are elected from single-member districts for four-year terms. Each commissioner must be a registered voter and live within the district they represent. Terms are staggered so that three commissioners are elected in one election cycle, and the other two members are elected in the next election cycle two years later.
The County Commission employs a County Administrator, who serves as its chief administrative officer. It is the responsibility of the County Administrator to carry out the policies and directives of the Commission, and for the development and management of the County's annual operating budget. The Administrator serves as the budgetary agent for all county offices. The County Administrator is also responsible for the supervision and management of various department heads, and for ensuring that all agreements, leases and other contractual obligations of the Commission are properly performed. The County Administrator works with Lee County Commissioners and other elected county officials to facilitate the delivery of quality and effective services to the citizens of Lee County.[11]
Lee County is very conservative for a county dominated by a college town. While most such counties have swung heavily to the Democrats since the 1990s, Lee County has not supported a Democrat for president since 1960. The last Democrat to garner over 40 percent of the county's vote was Jimmy Carter in both of his election campaigns in 1976 and 1980. However, Bill Clinton tallied over 38 percent of the county's vote in both of his successful runs for president, as did Barack Obama in both of his campaigns.
| Year | Republican | Democratic | Third party | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | % | No. | % | No. | % | |
| 2020 | 42,221 | 59.09% | 27,860 | 38.99% | 1,368 | 1.91% |
| 2016 | 34,617 | 58.48% | 21,230 | 35.87% | 3,344 | 5.65% |
| 2012 | 32,194 | 59.08% | 21,381 | 39.23% | 921 | 1.69% |
| 2008 | 32,230 | 59.33% | 21,498 | 39.57% | 597 | 1.10% |
| 2004 | 27,972 | 62.70% | 16,227 | 36.38% | 411 | 0.92% |
| 2000 | 22,433 | 58.63% | 14,574 | 38.09% | 1,257 | 3.29% |
| 1996 | 17,985 | 54.15% | 12,919 | 38.90% | 2,310 | 6.95% |
| 1992 | 16,885 | 47.58% | 13,770 | 38.80% | 4,835 | 13.62% |
| 1988 | 17,180 | 64.39% | 9,078 | 34.02% | 425 | 1.59% |
| 1984 | 16,757 | 64.05% | 9,077 | 34.70% | 327 | 1.25% |
| 1980 | 10,982 | 49.98% | 9,606 | 43.72% | 1,384 | 6.30% |
| 1976 | 9,884 | 52.75% | 8,427 | 44.98% | 426 | 2.27% |
| 1972 | 11,571 | 74.94% | 3,622 | 23.46% | 248 | 1.61% |
| 1968 | 2,366 | 18.01% | 2,803 | 21.34% | 7,967 | 60.65% |
| 1964 | 5,914 | 78.69% | 0 | 0.00% | 1,602 | 21.31% |
| 1960 | 2,301 | 37.73% | 3,759 | 61.63% | 39 | 0.64% |
| 1956 | 1,586 | 31.40% | 3,302 | 65.37% | 163 | 3.23% |
| 1952 | 1,626 | 36.67% | 2,803 | 63.22% | 5 | 0.11% |
| 1948 | 258 | 12.86% | 0 | 0.00% | 1,749 | 87.14% |
| 1944 | 134 | 6.23% | 2,011 | 93.49% | 6 | 0.28% |
| 1940 | 103 | 3.85% | 2,566 | 95.96% | 5 | 0.19% |
| 1936 | 93 | 4.07% | 2,183 | 95.62% | 7 | 0.31% |
| 1932 | 103 | 4.90% | 1,988 | 94.53% | 12 | 0.57% |
| 1928 | 1,016 | 41.38% | 1,436 | 58.49% | 3 | 0.12% |
| 1924 | 98 | 6.52% | 1,290 | 85.77% | 116 | 7.71% |
| 1920 | 155 | 8.19% | 1,620 | 85.58% | 118 | 6.23% |
| 1916 | 42 | 2.90% | 1,369 | 94.67% | 35 | 2.42% |
| 1912 | 43 | 3.25% | 1,179 | 88.98% | 103 | 7.77% |
| 1908 | 64 | 5.02% | 1,126 | 88.38% | 84 | 6.59% |
| 1904 | 40 | 2.80% | 1,348 | 94.40% | 40 | 2.80% |
| 1900 | 1,026 | 36.04% | 1,718 | 60.34% | 103 | 3.62% |
| 1896 | 1,491 | 43.83% | 1,737 | 51.06% | 174 | 5.11% |
| 1892 | 318 | 7.14% | 2,760 | 61.99% | 1,374 | 30.86% |
| 1888 | 1,432 | 41.80% | 1,991 | 58.11% | 3 | 0.09% |
Education[]
Lee County is home to Auburn University, a large comprehensive public university, and Southern Union State Community College, a two-year degree and technical college.
Communities[]
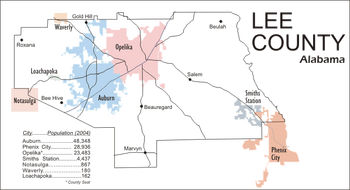

Population distribution in Lee County by municipality, 2010
Cities[]
- Auburn
- Opelika (county seat)
- Phenix City (partly in Russell County)
- Smiths Station
Towns[]
- Loachapoka
- Notasulga (partly in Macon County)
- Waverly (partly in Chambers County)
Unincorporated communities[]
- Beans Mill
- Beauregard
- Bee Hive
- Beulah
- Chewacla
- Gold Hill
- Hopewell
- Marvyn
- Roxana
- Salem
- The Bottle
Places of interest[]
Lee County is home to Auburn University Museum of Natural History, Chewacla State Park, the Jule Collins Smith Museum of Fine Art, Bean's Mill, the Salem-Shotwell Covered Bridge and the Grand National Golf course which is part of the Robert Trent Jones Golf Trail.
Gallery[]
|
See also[]
- List of memorials to Robert E. Lee
- National Register of Historic Places listings in Lee County, Alabama
- Properties on the Alabama Register of Landmarks and Heritage in Lee County, Alabama
References[]
- ^ a b "QuickFacts: Lee County, Alabama; Population, Census, 2020 & 2010". United States Census Bureau. https://www.census.gov/quickfacts/fact/table/leecountyalabama/POP010220.
- ^ "Find a County". National Association of Counties. http://www.naco.org/Counties/Pages/FindACounty.aspx.
- ^ Gannett, Henry (1905). The Origin of Certain Place Names in the United States (Report). U.S. Geological survey. Bulletin no. 258 (2nd ed.). Washington: Government Printing Office. p. 184. OCLC 1156805. https://archive.org/stream/bulletinofunited258gann#page/n189/mode/2up.
- ^ "2010 Census Gazetteer Files". United States Census Bureau. August 22, 2012. http://www2.census.gov/geo/docs/maps-data/data/gazetteer/counties_list_01.txt.
- ^ "U.S. Decennial Census". United States Census Bureau. https://www.census.gov/programs-surveys/decennial-census.html.
- ^ "Historical Census Browser". University of Virginia Library. http://mapserver.lib.virginia.edu.
- ^ Forstall, Richard L., ed (March 24, 1995). "Population of Counties by Decennial Census: 1900 to 1990". United States Census Bureau. https://www.census.gov/population/cencounts/al190090.txt.
- ^ "Census 2000 PHC-T-4. Ranking Tables for Counties: 1990 and 2000". United States Census Bureau. April 2, 2001. https://www.census.gov/population/www/cen2000/briefs/phc-t4/tables/tab02.pdf.
- ^ a b "U.S. Census website". United States Census Bureau. https://www.census.gov.
- ^ "Explore Census Data". https://data.census.gov/cedsci/table?g=0500000US01081&tid=DECENNIALPL2020.P2.
- ^ Text on Lee County government used with permission of Lee County Commissioners Office.
- ^ "Dave Leip's Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections". http://uselectionatlas.org/RESULTS/.
Further reading[]
- Barnes, Margaret Anne (1998). The Tragedy and the Triumph of Phenix City, Alabama. Macon, GA: Mercer University Press. ISBN 0-86554-613-4
- Nunn, Alexander (Ed.) (1983). Lee County and Her Forebears. Montgomery: Herff Jones. LCCN
 83081693-{{{3}}}
83081693-{{{3}}}
- Wright, John Peavy (1969). Glimpses into the past from my Grandfather's Trunk. Alexander City: Outlook Publishing Company, Inc. LCCN
 74101331-{{{3}}}
74101331-{{{3}}}
External links[]
|
Tallapoosa County | Chambers County | Harris County, Georgia | 
|
| Muscogee County, Georgia | ||||
 Lee County, Alabama | ||||
| Macon County | Russell County |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| This page uses content from the English language Wikipedia. The original content was at Lee County, Alabama. The list of authors can be seen in the page history. As with this Familypedia wiki, the content of Wikipedia is available under the Creative Commons License. |






