| Main | Births etc |
|---|
| Schiedam | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| — City and Municipality — | |||
| Old city hall of Schiedam | |||
|
|||
| Nickname(s): Brandersstad | |||
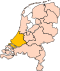
| Location in South Holland | |||
| Coordinates: Coordinates: | |||
| Country | Netherlands | ||
| Province | South Holland | ||
| Settled | c. 1230 | ||
| City rights | 1275 | ||
| Government[1] | |||
| • Body | Municipal council | ||
| • Mayor | Cor Lamers (CDA) | ||
| Area[2] | |||
| • Total | 19.86 km2 (7.67 sq mi) | ||
| • Land | 18.02 km2 (6.96 sq mi) | ||
| • Water | 1.84 km2 (0.71 sq mi) | ||
| Elevation[3] | −1 m (−3.3 ft) | ||
| Population (May 2013)[4] | |||
| • Total | 76,405 | ||
| • Density | 4,240/km2 (11,000/sq mi) | ||
| Demonym | Schiedammer | ||
| Time zone | CET (UTC+1) | ||
| • Summer (DST) | CEST (UTC+2) | ||
| Postcode | 3100–3125 | ||
| Area code | 010 | ||
| Website | schiedam.nl | ||

Dutch Topographic map of Schiedam, as of Sept. 2014

View of Schiedam with The Porters' Guild House

A windmill in Schiedam
Schiedam ([sxiˈdɑm] ( listen)) is a city and municipality in the province of South Holland in the Netherlands. It is part of the Rotterdam metropolitan area. The city is located west of Rotterdam, east of Vlaardingen, and south of Delft. In the south it is connected with the village of Pernis by the Beneluxtunnel.
The city is known for its historical center with canals, and for having the tallest windmills in the world. Schiedam is also well known for the distilleries and malthouses and production of jenever (gin) − such as the internationally renowned Ketel One − so much so that in French and English the word schiedam (usually without a capital s-) refers to the town's Holland gin. This was the town's main industry during the early Industrial Revolution in the 18th and 19th century, a dark period to which it owed its former nickname "Zwart Nazareth" or "Black Nazareth". Furthermore, the city is known for Saint Lidwina, one of the most famous Dutch saints (her relics are located in the Liduina Basilica in Schiedam).
History[]
Schiedam was founded in roughly the same way as its big neighbour Rotterdam; around the year 1230 the river Schie was dammed by the Lord of Wassenaer and the Amtlord Dirk Bokel of the Amt Mathenesse, this to protect the existing polderland against the seawater from the North Sea. In 1247, Lady Adelaide (Aleida) of Holland married John I, Count of Hainaut. As dowry she received from him the eastern part of the dam together with the adjacent polder. The dam attracted many trade activities because goods for and from the hinterland (Delft, and further away Leiden and Haarlem) had to be transhipped. A small town developed swiftly around the dam and its activities. In the year 1275 Schiedam received city rights from Lady Adelaide, this in her capacity as sister of William II, the reigning Count of Holland and becoming King of the Romans. She ordered the building of a castle near the Schie, which is known till today as the "Castle Mathenesse" (Dutch: "Huis te Riviere" or "Slot Mathenesse"). Remnants of a donjon, which were once part of the castle, are still visible today in the centre of Schiedam and near the city office.
As a young settlement Schiedam soon got competition from surrounding towns and cities: in 1340, Rotterdam and Delft also were allowed to establish a connection between the Schie and the Meuse. From the 15th century on the city flourished as a place of pilgrimage on the devotion around Saint Lidwina, one of the most famous Dutch saints who lived her life in Schiedam. The city gained subsequently significance by fishing for herring. In 1428 a great city fire swept through Schiedam, thereby destroying large parts of the then wooden city .
The 18th century was Schiedam's Golden Age, when the gin industry flourished. The standstill drink imports from France made the emergence of the Schiedamse distillery possible. From dozens of distilleries Schiedam jenever was exported throughout the world. The gin industry gave the city its nickname 'Black Nazareth'. This industry is now largely gone. Five windmills in the town, called De Noord, Walvisch, Drie Koornbloemen, Nieuwe Palmboom and Vrijheid − the highest windmills in the world because they had to stick out above the high warehouses, and many storehouses are relicts of this past. In one of the former factories at the Lange Haven the National Jenever Museum is established.
On 10 August 1856 the first major train accident in the Netherlands happened near the Schiedam railway station, causing 3 deaths. On 4 May 1976 the Schiedam train disaster took place near the station which caused 24 deaths.[5]
At the end of the 19th and throughout the 20th century, the shipbuilding industry was booming in Schiedam, with the existence of large companies like Wilton-Fijenoord and others. In 1941, the ancient municipalities Kethel en Spaland were merged with Schiedam which made large expansions of the city possible with residential areas in the north. At the end of the 20th century the shipbuilding industry largely disappeared and nowadays Schiedam is mainly a commuter town being part of the Rotterdam metropolitan area.
Geography[]
The city of Schiedam is located in the Dutch province of South Holland. It is enclosed between Rotterdam (east), Midden-Delfland (north), Vlaardingen (west) and the river Nieuwe Maas (south).
Demographics[]
Historical population[]
- 1990 − 69,417
- 1995 − 73,480
- 2000 − 75,589
- 2005 − 75,487
- 2010 − 75,565
- 2013 − 76,216
Source: CBS[6]
Composition[]
Schiedam exists of nine districts: Centrum ('Center'), Oost ('East'), Gorzen ('South'), West ('West'), Nieuwland, Groenoord, Kethel, Woudhoek and Spaland/Sveaparken.[7]
Ethnic make-up[]
| Descent | 1996 | 2000 | 2005 | 2012 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dutch | 78,1% | 73,6% | 69,1% | 63,8% |
| Foreign | 21,9% | 26,4% | 30,9% | 36,2% |
| Turkish | 6,8% | 7,7% | 9,1% | 10,1% |
| Surinamese | 2,3% | 2,7% | 3,1% | 3,5% |
| Moroccan | 1,5% | 1,8% | 2,3% | 2,9% |
| Antillean | 0,8% | 1,4% | 2,1% | 2,4% |
Source: CBS[8]
Attractions[]
Museums[]
- Het Stedelijk Museum
- Jenever Museum
- Het Borrelmuseum (in 't Spul on Hoogstraat)
- Museummolen De Nieuwe Palmboom
- Nationaal Coöperatie Museum Schiedam / 't Winkeltje
- Artgallery 't Walvisch
Monuments[]
- The old city hall (Het Oude stadhuis) (photo)
- The canals of Schiedam
- The Wheat Exchange (De Korenbeurs)
- Church of Saint John (Grote of Sint-Janskerk)
- The ruins of the castle Huis te Riviere (photo)
- Saint Lidwina basilica (photo)
- De Plantage (a park)
- The Porters' Guild House (Het Zakkendragershuisje)
- Het Proveniershuis (housing elderly people)
- The historical windmills of Schiedam. This includes the tallest windmill in the world which is used as a restaurant.
Events[]
- De Brandersfeesten
- The National Windmill Days (Nationale Molen- & Gemalen dag)
- Lipdub Schiedam 2012 DOUBLE LIPDUB WORLD RECORD!!!
Sport[]
The most popular sports in Schiedam are soccer and field hockey. Cricket is more popular in Schiedam than in most other Dutch cities.[9]
Notable residents[]

Jan van Riebeeck grew up in Schiedam
- Maarten Biesheuvel (born 1939) − writer
- Rob Cordemans (born 1974) − baseball player
- Luc Castaignos (born 1992) − footballer
- Rinus Gosens (1920–2008) − footballer
- Herman Heinsbroek (born 1951) − entrepreneur and former Dutch Minister of Economic Affairs
- Erik Jazet (born 1971) − hockey player and coach
- Ali Elkhattabi (born 1977) − footballer
- Danny Koevermans (born 1978) − footballer
- Saint Lidwina (1380–1433) − Catholic saint
- Robert Maaskant (born 1969) − footballer
- Piet Paaltjens (pen name of Francois Haverschmidt) (1835–1894) − Protestant clergyman and romantic author
- Rien Poortvliet (1932–1995) − sketcher and painter
- Jan van Riebeeck (1619–1677) − colonial administrator and founder of Cape Town, South Africa.
- Gökhan Saki (born 1983) − kickboxer
- Jos van Emden (born 1985) − cyclist
- Andre van Troost (born 1972) − cricketer
- Luuk van Troost (born 1969) − cricketer
- Pieter van Vollenhoven (born 1939) − husband of Princess Margriet of the Netherlands
- Pauline van der Wildt (born 1944) − swimmer
- Elizabeth Witmer (born 1946) − member of the Legislative Assembly of Ontario, Canada
- John de Wolf (born 1962) − footballer
International relations[]
Twin towns – Sister cities[]
Schiedam is twinned with:
All these contacts were under review after a decision of the municipal council on 4 February 2010 [11]
- Schiedam is a member city of Eurotowns network[12]
References[]
- ^ "Dhr. C.H.J. Lamers [Mr. C.H.J. Lamers]" (in Dutch). Gemeente Schiedam. http://www.schiedam.nl/Def/Overheids-Modules/BIS-Module-30/Bestuur-en-organisatie/Lamers.html. Retrieved 23 August 2013.
- ^ "Kerncijfers wijken en buurten [Key figures for neighbourhoods]" (in Dutch). CBS Statline. CBS. 2 July 2013. http://statline.cbs.nl. Retrieved 11 July 2013.
- ^ "Postcodetool for 3112DZ" (in Dutch). Actueel Hoogtebestand Nederland. Het Waterschapshuis. http://www.ahn.nl/postcodetool. Retrieved 23 August 2013.
- ^ "Bevolkingsontwikkeling; regio per maand [Population growth; regions per month]" (in Dutch). CBS Statline. CBS. 24 June 2013. http://statline.cbs.nl/StatWeb/publication/?DM=SLNL&PA=37230NED&D1=17-18&D2=101-619,621,624-632&D3=l&LA=EN&HDR=T&STB=G1,G2&VW=T. Retrieved 11 July 2013.
- ^ "Eerste treinramp met doden ook bij Schiedam" (in nl). Dagblad van het Noorden. May 1, 2004. http://www.archiefleeuwardercourant.nl/vw/article.do?id=DVHN-20040501-DW01006004&vw=org&lm=treinramp%2Cschiedam. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ http://statline.cbs.nl/StatWeb/publication/?DM=SLNL&PA=03759ned&D1=0,3,6,9,12&D2=129-132&D3=700&D4=a&HDR=T&STB=G2,G3,G1&VW=T
- ^ http://www.schiedam.nl/Def/inwoners/Wonen-en-Wijken/Wijken.html
- ^ http://statline.cbs.nl/StatWeb/publication/?DM=SLNL&PA=37713&D1=0-8&D2=0&D3=1-2,6-55&D4=611&D5=0,4,9,15-16&HDR=T,G4&STB=G1,G3,G2&VW=T
- ^ FT.com / Arts & Weekend / Sport - Hail Holland, world cricket's unlikely lads
- ^ "Neath Port Talbot Twin Towns". Neath Port Talbot County Borough Council. http://www.npt.gov.uk/default.aspx?page=1988. Retrieved 2013-08-22.
- ^ [1] Decision municipal councel (in Dutch)
- ^ "Eurotowns". http://eurotowns.org.
External links[]
| Find more about Schiedam on Wikipedia's sister projects: |
| Source texts from Wikisource | |
| Images and media from Commons |
|
Midden-Delfland | 
| ||
| Vlaardingen | Rotterdam | |||
 Schiedam | ||||
| Nieuwe Maas Rotterdam |
| |||||||||||
|
| This page uses content from the English language Wikipedia. The original content was at Schiedam. The list of authors can be seen in the page history. As with this Familypedia wiki, the content of Wikipedia is available under the Creative Commons License. |