| ||||||||||||||
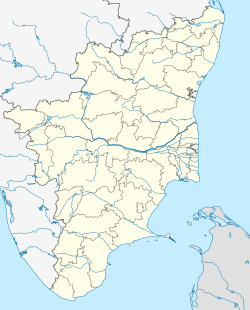
| Erode district ஈரோடு மாவட்டம் Periyar District |
|
|---|---|
| — District — | |
| Confluence of the Bhavani and Kaveri Rivers | |
| Coordinates: Coordinates: | |
| Country | India |
| State | Tamil Nadu |
| Region | Western Tamil Nadu (Kongu Nadu) |
| Division | Coimbatore |
| District | Erode |
| Metro | |
| Established in | 1979 |
| Headquarters | Erode |
| Talukas | Erode, Gobichettipalayam |
| Government | |
| • Collector | Mr C. Kamaraj IAS |
| Area | |
| • District | 5,692 km2 (2,198 sq mi) |
| Population (2011)[1] | |
| • District | 22,59,608 |
| • Density | 397/km2 (1,030/sq mi) |
| • Metro | 1,500,000 |
| Languages | |
| • Official | Tamil |
| Time zone | IST (UTC+5:30) |
| PIN | 638*** |
| Telephone code | 0424/04204/04256/04285/04295 |
| Vehicle registration | TN-33/36/56 [2] |
| Largest city | Erode |
| Sex ratio | M-51%/F-49% ♂/♀ |
| Literacy | 72.96% |
| Lok Sabha seats | 3 |
| Vidhan Sabha seats | 8 |
| Central location: | |
| Precipitation | 700 millimetres (28 in) |
| Avg. summer temperature | 35 °C (95 °F) |
| Avg. winter temperature | 18 °C (64 °F) |
| Website | erode.tn.nic.in |
Erode District is a western district of the state of Tamil Nadu, India, with Erode as its headquarters. Until the year 1996, Erode district was called as Periyar District.
Erode District was a part of Coimbatore District until September 17, 1979. Mathematician Ramanujan and social reformer Periyar were from here.
Erode district had a population of 22,59,608 as of 2011. It is 46.25% urbanised as per Census 2001.[3] The district has a literacy rate of 72.96% and is on the rise.
Geography[]

Typical streetlife in Erode, capital of Erode district.
The district is bounded by Chamarajanagar district of Karnataka to the north, and by Kaveri River to the east. Across the Kaveri lies Salem, Namakkal and Karur districts. Tirupur District lies immediately to the south, and Coimbatore and the Nilgiris district lies to the west. Erode District is landlocked and is situated at between 10 36” and 11 58” north latitude and between 76 49” and 77 58” east longitude.
The district comprises a long undulating plain, sloping gently towards the Kaveri river in the south-east. Three major tributaries of river Kaveri, the Bhavani, Noyyal and Amaravati, run across the long stretch of mountains in the north. Other significant rivers are Palar in the north and Vatamalaikarai odai and Uppar rivers in the south. The Palar constitutes the boundary between Erode district and Karnataka in the north. The Bhavanisagar dam and Kodiveri dam provide storage facilities and numerous canals along with these rivers provide proper drainage and facilities for irrigation in the district.
Bhavani River[]
Bhavani rises in the Western Ghats of Silent Valley National Park in Palakkad District of Kerala. It receives the Siruvani River which has the second tastiest water in the world, a perennial stream of Coimbatore District, and gets reinforced by the Kundah river before entering Erode District in Sathyamangalam. Bhavani is more or less a perennial river fed mostly by the southwest monsoon. The northeast monsoon also supplements its water resources. This river runs for over hundred miles through Erode District, traversing Bhavani and Gobichettipalayam taluks. It feeds the Bhavanisagar reservoir, which takes an easterly course after Sathyamangalam taluk. Between Sathyamangalam and Gobichettipalayam lies the Kodiveri Dam, a mini dam constructed for agricultural purposes. Then it flows through Gobichettipalayam and Bhavani taluks before it ultimately joins Kaveri in the island of Bhavani, Tamil Nadu, near Erode, with a holistic tributary river of Amutha Nathi, hence called Tiriveni Sangamam. The place where Bhavani joins with Kaveri River is famous for Sri Sangameshwara Temple of Lord Shiva, where according to the Hindu customs people perform the last rights for deceased near and dears.
Kaveri River[]

Kaveri river in Erode district
Kaveri rises in the Western Ghats of Kodagu (Coorg) District, in Karnataka, and is joined by many small tributaries. It runs eastward through Karnataka, and at Hogenakal fall takes a sharp turn, east to south. Before reaching this point, it is joined by its main tributary, the Kabini River. From here it runs towards the southeast, forming the boundary between Bhavani Taluk of Erode District and Tiruchengode Taluk of the neighbouring Namakkal District. The Bhavani River joins the Kaveri at the town of Bhavani.
Noyyal River[]
Noyyal river is noted for its capricious nature. This is fed mostly by the southwest monsoon but the northeast monsoon brings freshes, and this very often results in floods. In spite of its unpredictable character, the river helps to irrigate considerable areas in Palladam taluk of Coimbatore District and Kangeyam taluk of Erode District.But due to the chemical waste came from tirupur dying factories this river water cannot used for the agriculture.
Amaravati River[]
Amaravati river rises in the Travancore region of Kerala, and enters Erode District from Udumalaippettai taluk in Coimbatore District. The river flows through Dharapuram and Kangeyam taluk before it joins Kaveri in Karur District.
Hills[]
Western Ghats traverses across the district giving rise to small hill locks namely:
- Chennimalai
- Pachaimalai and Pavazhamalai
- Perumalmalai
- Thalavumalai
- Lakkapuram Hills
- kaithamalai
Tourist and Pilgrim Centres[]
Important Tourist Centres
- Bhavanisagar Dam, Bhavanisagar
- Kodiveri Dam, Gobichettipalayam
- Bhavani Kooduthurai, Bhavani
- Periyar Memorial House, Erode
- Erode Museum, Erode
- Birds sanctuary, Vellode, Erode
- Cavuey Padakuthurai (Boat House), Kodumudi
Important Pilgrim Centres
- Bhavani Sangameswarar Temple, Bhavani
- Pariyur Kondathu Kaliamman Temple, Amarapaneeswarar Temple and Adinarayana Swamy Temple, Pariyur, Gobichettipalayam
- Bannari Mariamman Temple, Bannari
- Periya Mariamman Temple, Erode
- Thindal Murugan Temple, Erode
- Cinna Amman and Periya Amman Temple in Mugasi Anuman palli {Vellode-Arachalur via}
- Balamurugan Temple, Pachaimalai and Muthukumaraswamy Temple, Pavalamalai, Gobichettipalayam
- Chennimalai Murugan Temple, Chennimalai
- Magudeswarar Temple, Kodumudi
- Velayuthaswami Temple and Sri Ponkaliamman Temple, Sivagiri
- Vijayapuriamman Temple, Vijayamangalam
- Jain Temple, Vijayamangalam
- Gurunathaswamy Temple, Anthiyur
- Badhrakali Amman Temple, Anthiyur
- Malai Karuppusamy Temple, Anthiyur Colony
Climate[]
The climate is mostly dry and characterised by good rainfall. Unlike nearby Coimbatore district, Erode District has dry weather throughout the year except during the monsoons. The Palghat Gap in Western Ghats, which has a moderating effect on the climate of Coimbatore district, does not help in bringing down the dry climate in this area. The cool moist wind that gushes out of the west coast through Palghat gap loses its coolness and becomes dry by the time it crosses Coimbatore district and reaches Erode.
Generally the first two months of the year are pleasant, but in March the temperature begins to rise, which persists till the end of May. The highest temperatures are normally recorded during May. The scanty showers during this period do not provide much relief from the oppressive heat. However, there is an improvement in the climate during the June–August period. During the pre-monsoon period, the temperature reverses its trend. By September the sky gets heavily overcast, although the rains pour down. The northeast monsoon sets in vigorously only during October–November, and by December the rains disappear, rendering the climate clear and cold.
Administration[]
Erode District is separated into 2 revenue divisions
- Erode
- Gobichettipalayam
Erode District consists of 5 Taluks
- Bhavani
- Erode
- Gobichettipalayam
- Perundurai
- Sathyamangalam
Erode District consists of 6 Municipalities
Selection Grade Municipality:
- Gobichettipalayam
Grade I Municipality:
- Sathyamangalam
Grade II Municipality:
- Bhavani
- Perundurai
- Punjai Puliampatti
Grade III Municipality:
- Kasipalayam, Erode
Erode District is divided between 3 Parliamentary Constituencies
- Erode Parliamentary Constituency
- Nilgiris Parliamentary Constituency
- Tirupur Parliamentary Constituency
Erode District consists of 8 Assembly Constituencies
- Anthiyur
- Bhavani
- Bhavani Sagar
- Erode East
- Erode West
- Gobichettipalayam
- Modakurichi
- Perundurai
Economy[]
Agriculture is the most important income source of this district. Paddy, Plantain, Groundnut, cotton, turmeric, coconut and sugarcane are some of the agricultural products. With 43% share, the district is the top turmeric producer in Tamil Nadu.[1]. Erode is also known as "The Turmeric City". Erode District is an important market centre for turmeric, a spice commonly used in curries. Turmeric is also used as a fabric dye. The turmeric is collected from Erode District and from adjoining districts of Tamil Nadu and Karnataka, including Mysore. Erode district is also the leading producer of plantain, coconuts and white silk in Tamil Nadu.

Fabrics, like rugs, made in Erode are famous in India.
Gobichettipalayam is well known for its white silk, plantain and coconut production. The country's first automated silk reeling unit is in Gobichettipalayam.
Erode is also well known for handloom, powerloom textile products and ready-made garments and hence called the powerloom city of India. Products such as cotton sarees, bed spreads, carpets, lungies, printed fabrics, towels, dhotis are marketed there. In mid-2005, Bhavani Jamakkalam (Bhavani Bedsheets) was registered as a Geographical Indication by the Government of India. Nowadays more and more spinning mills which produce yarn for the power loom are set up in and around the town of Erode. Chennimalai is also famous for textiles.

Turmeric powder, used extensively in Indian cuisine
Punjai Puliampatti has the second largest weekly shandy in Tamil Nadu and it is one of the leading tobacco producers in Tamil Nadu. Anthiyur shandy and Modachur shandy are famous for cattle.
Transportation[]

Erode railway junction.
The transportation system in the district is already well developed. Erode, being one of the prominent trading centres in the state, is well connected with all modern means of transport except air transport. The district is accessible by both road and rail from the state capital Chennai and other district headquarters.
Rail Transport
Erode junction was a important railway station built by the British to connect the west coast of India to the east coast of India. There is a diesel locomotive shed and an electric locomotive shed for Erode Junction. It is one of the most important railway stations in India. The station code is ED. It has state of the art technology in electrification and was the first electrified link from Chennai with broad gauge conversion. Erode Junction has the distinction of being the Third cleanest railway junction in India, after Bhopal Habibganj Railway Station (Bhopal) and Secunderabad Railway Station (Hyderabad) in India. Both Electric and Diesel Locomotive Sheds have been ISO certified. It also serves as the hub for water filling facilities, food provision and toilet cleaning to all long distance trains that run via Erode. Erode Junction is the junction point between the trains passing towards West/East of Tamil Nadu and Kerala, Karnataka with 4 platforms and it one of the busiest railway junctions where many trains passing through. The station is well connected by buses round the clock. There are Five local railway stations in the city.
Road Transport
Tamil Nadu State Transport Corporation Coimbatore div-II headquartered at Erode originally called as Jeeva Transport Corporation(JTC) Ltd services the inter and intra city routes. The Erode division of the TNSTC services the district's road transport needs with a string of local and mofussil (out-of-town) services. The State Express Bus Corporation (SETC) operates express services to Chennai, Coimbatore, Mysore, Cochin, Thrissur, Salem, Bangalore, Pondicherry, Nagapattinam, Vellore, Tirunelveli, and Tirupati. One can get buses from Erode to almost any part of the state. Erode bus stand is the second largest in Tamil Nadu in terms of area after CMBT, Chennai.

Busiest Arterial Road of the city - Brough Road
TNSTC - ERODE
The Tamil Nadu State Transport Corporation (TNSTC) has a divisional headquarters at Erode. Originally called as Jeeva Transport Corporation (JTC), it came into being by bifurcation of the Cheran Transport Corporation (headquartered at Coimbatore). It started functioning from 1 April 1983, with the principal area of operation in the Erode District, parts of Tirupur, Namakkal, Salem and Karur Districts. It was renamed as Tamil Nadu State Transport Corporation, Erode Limited (Coimbatore Division-II) on 1 July 1997. The fleet strength as on 31 March 2005 was 1218 during the year 2003-2005. It has many depots at various places in the districts are Erode-1, Erode-2, Erode-3, Bhavani, Gobichettipalayam, Anthiyur, Perundurai, Nambiyur, Sathyamangalam, Kavindapadi, Thalavadi, Karur and proposed depots at Kodumudi and Chennimalai.
Distances from Erode[]
| Sl no | Town | Distance (km) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Anthiyur | 40 |
| 2 | Bhavani | 15 |
| 3 | Chennampatti | 50 |
| 4 | Chennimalai | 35 |
| 5 | Gobichettipalayam | 35 |
| 6 | Perundurai | 20 |
| 7 | Kodumudi | 40 |
| 8 | Sathyamangalam | 65 |
| 9 | Bhavanisagar | 65 |
| 10 | Thalavadi | 120 |
| 11 | Sivagiri | 35 |
| 12 | Nambiyur | 65 |
| 13 | Arachalur | 25 |
| 14 | Hasanur | 125 |
- Highways
National Highways
- NH-47 connecting Chennai – Salem – Coimbatore – Cochin – Kanyakumari passes via Bhavani, Chithode and Perundurai
- NH-209 connecting Bangalore – Coimbatore – Dindigul passes via Sathyamangalam
Proposed Highways
- NH 67-A, which splits from Karur to Erode, and reaches Mysore through Gobichettipalayam, Sathyamangalam and Chamarajanagar and to Bangalore through Anthiyur & Kanakapura.
- NH 209-A, connecting Sathyamangalam – Gobichettipalayam – Erode – Karur - Dindigul.
State Highways
- SH-15 connecting Erode – Gobichettipalayam – Sathyamangalam – Mettupalayam - Ooty
- SH-20 connecting Erode – Bhavani – Mettur Dam – Mecheri – Thoppur (om NH-7)
- SH-37 connecting Mettur – Erode – Kangeyam – Dharapuram – Palani
- SH-79 connecting Erode – Tiruchengode – Rasipuram – Attur
- SH-81 connecting Gobichettipalayam – Uthukuli – Kangeyam – Dharapuram
- SH-82 connecting Sathyamangalam – Athani – Bhavani
- SH-84 connecting Erode – Kodumudi – Karur
- SH-84A connecting Erode – Modakurichi – Moolanur
- SH-96 connecting Erode – Perundurai – Chennimalai – Kangeyam
Air Transport
- Coimbatore International Airport, which is 85 km (53 mi) by road
- Salem Airport, which is 65 km by road
Other modes Navigable waterways are available at five places in the district.
Demographics[]
According to the 2011 census Erode district has a population of 2,259,608,[4] roughly equal to the nation of Latvia[5] or the US state of New Mexico.[6] This gives it a ranking of 200th in India (out of a total of 640).[4] The district has a population density of 397 inhabitants per square kilometre (1,030 /sq mi) .[4] Its population growth rate over the decade 2001-2011 was 12.05 %.[4] Erode has a sex ratio of 992 females for every 1000 males,[4] and a literacy rate of 72.96 %.[4]
Communication[]
The district is also served by an extensive Postal, Telegraph and Telephone networks. It is connected to the rest of the state by subscriber trunk dialing system (STD). The telephone network within the city is also expanding rapidly.
- Postal Divisions : 2 (Erode, Gobichettipalayam)
- Head Post offices : 3 (Erode, Bhavani and Gobichettipalayam)
- Other Post offices : 319 (including extra departmental sub-post offices and telegraph offices)
- Post and Telegraph offices : 144
- Post offices with phone facilities : 144
The district has a vast coverage by mobile phone operators.Since most of its people live in rural areas it is far more economical for the people as well as the mobile operators to build the infrastructure for mobile phone communications.
Education[]
Erode district has several facilities for higher education including a Medical College, fifteen Engineering colleges along with 18 Arts and Science Colleges. It has two educational districts, Gobichettipalyam and Erode.
See also[]
- Erode
- Erode Municipal Corporation
- Erode Junction
- List of Educational Institutions in Erode
- Sivagiri, Erode
References[]
- ^ "2011 Census of India" (Excel). Indian government. 16 April 2011. http://www.censusindia.gov.in/2011-prov-results/prov_data_products_tamilnadu.html.
- ^ www.tn.gov.in
- ^ Census 2001
- ^ a b c d e f "District Census 2011". Census2011.co.in. 2011. http://www.census2011.co.in/district.php. Retrieved 2011-09-30.
- ^ US Directorate of Intelligence. "Country Comparison:Population". https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/rankorder/2119rank.html. Retrieved 2011-10-01. "Latvia 2,204,708 July 2011 est."
- ^ "2010 Resident Population Data". U. S. Census Bureau. http://2010.census.gov/2010census/data/apportionment-pop-text.php. Retrieved 2011-09-30. "New Mexico - 2,059,179"
External links[]
|
Chamarajanagar district, Karnataka | Dharmapuri district | 
| |
| Nilgiris district | Salem district | |||
 Erode district | ||||
| Coimbatore district | Tiruppur district | Namakkal district Karur district |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Template:Erode district
| This page uses content from the English language Wikipedia. The original content was at Erode district. The list of authors can be seen in the page history. As with this Familypedia wiki, the content of Wikipedia is available under the Creative Commons License. |